HEALTH AND FITNESS
Fonendi: A Doctor’s Go-To Diagnostic Device

“Fonendi” is a colloquial term widely used by medical professionals to refer to a phonendoscope, a sophisticated variation of the stethoscope designed to listen to internal body sounds such as heartbeats, breath sounds, and bowel activity. Though not an official clinical term, “Fonendi” has become commonplace in hospital corridors, medical colleges, and everyday doctor-patient conversations due to its ease of pronunciation and familiarity.
Derived out of the Greek, phono (sound), endo (within), and scope (to examine), the phonendoscope, or rather the Fonendi as it is commonly known derisively, is a major tool used in the auscultation stage of diagnosis. The design has facilitated the clearer amplification of internal sounds to enable the healthcare providers to have a better diagnosis of conditions like arrhythmias, respiratory obstructions, or gastrointestinal problems.
Table of Contents
Origin & Etymology
The late 19th century saw the term phonendoscope come up as an enhancement to the more primitive stethoscope that was not so good when it came to precision of sound. Based on the Greek language, phono means sound, endo refers to something internal, and scope means observation. With the development of language and medical practice, the term phonendoscope was coined in ruined circumstances to Fonendi, especially in those countries where the rapidity of communication is essential, and there are emergency rooms and teaching hospitals.
Types Comparison
| Type | Design | Primary Use | Sound Quality | Audience |
| Acoustic Fonendi | Traditional tubing with dual-head chestpiece | Basic auscultation | Moderate | Medical students, general physicians |
| Electronic Fonendi | Digital amplification and sound filters | Cardiology, pulmonary monitoring | High-fidelity | Specialists, researchers |
| Pediatric Fonendi | Smaller diaphragm and bell | Designed for children | Child-specific clarity | Pediatricians |
| Disposable Fonendi | Lightweight, for single-use environments | Infection control | Lower, adequate | Emergency, isolation wards |
Components in Detail
1. Chestpiece
The chest-piece is typically two-sided; the high-frequency side includes a diaphragm and the low-frequency side a bell. The diaphragm of a Fonendi can be tunable; that is, the pressure applied defines which frequency range is amplified.
2. Tubing
Fonendi tubing consists of thick non-latex PVC or other synthetic material. This keeps atmospheric noises to the bare minimum and creates a better flow of sound between the chestpiece and earpieces.
3. Earpieces
Comfort and sound isolation are made with the help of soft-sealing of Earpieces. Their angle of anatomical match is directed towards the ear canal, which allows maximum delivery of the sound and minimum discomfort when wearing the product over long periods.
4. Stem and Headset
The chestpiece is connected to the tubing by a metal stem, and the headset has in it binaural (metal tubes) through which sounds reach the ears. These parts are designed in order to be elastic but solid, so there is less likelihood to readjust them in the process of their use.
Professional Tips
- Clean Regularly: Prevent infections by sanitizing earpieces and chestpieces after each use.
- Store Properly: Avoid extreme temperatures that may degrade tubing material.
- Use Appropriate Pressure: Learn how diaphragm pressure alters frequency for optimal diagnosis.
- Replace Earpieces: Change them if they become loose or uncomfortable to preserve sound quality.
Everyday Utility
The Fonendi is required in clinical practice. Medical students bear it as a part of a rite-of-passage, nurses use it to check vitals, and experienced doctors use it to check any slight abnormalities. It turns out to be not just a tool; it is a connection point between intuition and evidence. It is broadly departmental, ranging between emergency rooms, cardiology clinics, and the general practice. It is an affordable, non-invasive wonder of a diagnosis in low-resource territories.
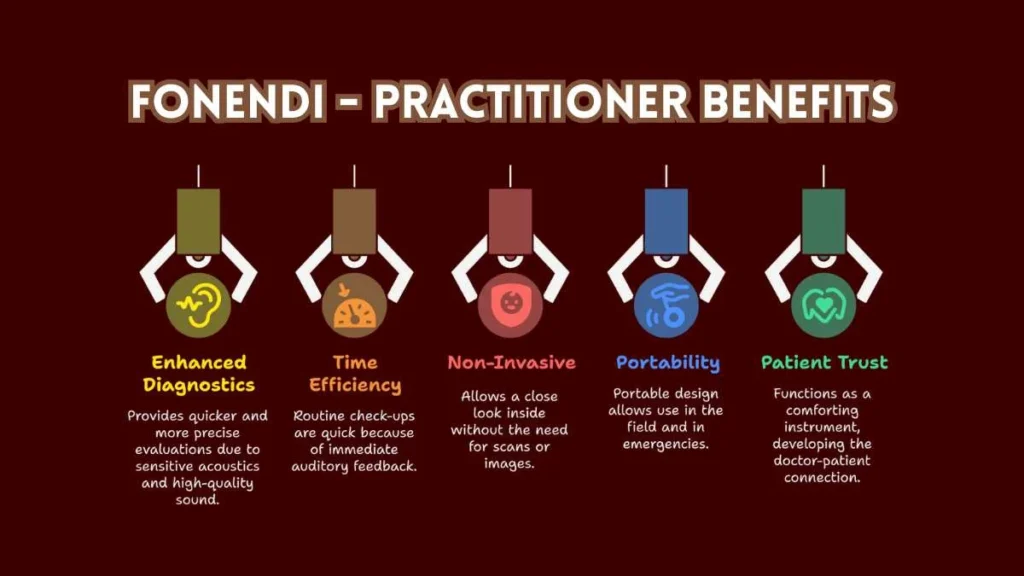
Benefits for Practitioners
- Enhanced Diagnostics: Sensitive acoustics and high-quality sound provide quicker and more precise evaluations.
- Time Efficiency: Routine check-ups are quick via immediate auditory feedback.
- Non-Invasive: It does not need scans or images to take a close look at the inside.
- Portability: It is portable and thus can be used in fields as well as in an emergency.
- Patient Trust: This functions as a comforting instrument that helps to develop the connection between the patient and the doctor during examination.
Global Usage
Whether it be hospitals in New York or a clinic in Pakistan, the Fonendi is a standard representation of medicine. Not very professional, nevertheless, the word “Fonendi” is immediately identified by cultures and medical communities. It symbolizes the importance of the tool as well as the imprint that the culture has placed on generations of people in the medical field.
First fond memories are passed down many times as an asset of medical students, and most doctors hang on to the first one as a remembrance. It remains synonymous with hands-on care, whether it is employed at an emergency room or at an academic classroom.
Conclusion
This might seem to be a medical topic which is not mentioned in the books, but concerning the daily practice, it is hard to doubt its importance. Being a slang alternative to phonendoscope, an indispensable diagnostics device, Fonendi represents not only a shift in the historical development of the medical vocabulary but also the historical continuity of using physical examination. With excellent sound clarity, ergonomic construction, and wide applicability, the Fonendi still plays a vital role in helping medical professionals to listen, diagnose, and heal. It could be applied in the crowded cities and in the rural clinics, but it remains silent in the hands of the life-saving heroes.
-

 FRIENDSHIP MESSAGES5 months ago
FRIENDSHIP MESSAGES5 months ago100+ Heart Touching Sorry Messages for Friends
-

 ANNIVERSARY WISHES8 months ago
ANNIVERSARY WISHES8 months ago100+ Beautiful Engagement Anniversary Wishes Messages and Quotes
-

 BIRTHDAY WISHES8 months ago
BIRTHDAY WISHES8 months ago300+ Happy Birthday Wishes for Brother | Heart Touching Happy Birthday Brother
-

 BIRTHDAY WISHES8 months ago
BIRTHDAY WISHES8 months ago200+ Unique Birthday Wishes for Your Best Friend to Impress on Their Big Day